During the Information Security week of the UC Baseline cybersecurity program, the instructors asked us a lot of questions whose answers we had to look up. As a way to maximize participation, we were encouraged to share lots of links of the class’ Slack channel, which also functioned as a backchannel, as well as a way to chat with the students who were taking the course online.
During the Information Security week of the UC Baseline cybersecurity program, the instructors asked us a lot of questions whose answers we had to look up. As a way to maximize participation, we were encouraged to share lots of links of the class’ Slack channel, which also functioned as a backchannel, as well as a way to chat with the students who were taking the course online.
The links that we shared in class were valuable material that I thought would be worth keeping for later reference. I’ve been spending an hour here and there, gathering them up and even organizing them a little. The end result is the list below.
Since these are all publicly-available links and don’t link to any super-secret UC Baseline instructional material, I’m posting them here on Global Nerdy. Think of this list as a useful set of security-related links, something to read if you’re bored, or a peek into what gets discussed during the InfoSec week of the UC Baseline course!
The links
- Security in general:
- Krebs on Security: Thinking of a Cybersecurity Career? Read This.
Krebs is a good regular read for security news, and this article is a good guide: “Thousands of people graduate from colleges and universities each year with cybersecurity or computer science degrees only to find employers are less than thrilled about their hands-on, foundational skills. Here’s a look at a recent survey that identified some of the bigger skills gaps, and some thoughts about how those seeking a career in these fields can better stand out from the crowd.” - Cybersecurity salary info:
- Some articles on recent breaches and how much money gets lost as a result of a data breach:
- 107 Must-Know Data Breach Statistics for 2020
- What is the Cost of a Data Breach in 2020?
- The 15 biggest data breaches of the 21st century
- All Data Breaches in 2019 & 2020 – An Alarming Timeline
- Cybercrime Magazine: Cybercrime Damages $6 Trillion By 2021
- Fortune: What getting hacked will cost you ($3.86 million, approximately)
- PII links:
- More breach links:
- Don’t use CCleaner:
- Student hacker plans for repl.it
repl.it is a web-based IDE/REPL that supports 50 programming languages and collaboration. Include tutorials, message boards and other “community” features. - GitHub student developer pack
Free subscriptions and software for students enrolled in an institution or program that they recognize. Loads of great offers; don’t miss this one. - NHS (Healthcare) Defense in Depth
A detailed chart showing the many layers of defense that are required for systems containing healthcare information. - Zero trust:
- Sound advice:
- Wired: The Garmin Hack Was a Warning
“Ransomware continues to affect the usual suspects; the hospitals and cities and homeowners who click on a bad link haven’t gotten any sort of reprieve. But as hacking groups add both to their coffers and tool sets, it seems likely that Garmin is hardly an outlier—and only a matter of time before the next big target takes a big fall.” - Department of Defense: Defense Critical Infrastructure Program (DCIP): DoD Mission-Based Critical Asset Identification Process (CAIP)
The DoD’s guidelines for identifying assets, a key part of security. - The O.MG cable
It looks, feels, and acts like an ordinary USB cable, but it also has a processor, web server, and 802.11 radio, which can help you sneak your way into a system. - GRC: Governance, Risk, and Compliance
“The acronym GRC was invented by the OCEG (originally called the ‘Open Compliance and Ethics Group’) membership as a shorthand reference to the critical capabilities that must work together to achieve Principled Performance — the capabilities that integrate the governance, management and assurance of performance, risk, and compliance activities.” - Éric Allaire’s CISSP aide-mémoire
Aide-mémoire is a pantalons-fancie term for “cheat sheet”. It’s a good security study guide. - The eJPT — eLearnSecurity Junior Penetration Tester certification
“The eJPT designation stands for eLearnSecurity Junior Penetration Tester. eJPT is a 100% practical certification on penetration testing and information security essentials. By passing the challenging exam and obtaining the eJPT certificate, a penetration tester can prove their skills in the fastest growing area of information security.” - NIST Cybersecurity Framework
“The Framework is voluntary guidance, based on existing standards, guidelines, and practices for organizations to better manage and reduce cybersecurity risk. In addition to helping organizations manage and reduce risks, it was designed to foster risk and cybersecurity management communications amongst both internal and external organizational stakeholders.” - NIST Special Publication 800-series General Information
“Publications in NIST’s Special Publication (SP) 800 series present information of interest to the computer security community. The series comprises guidelines, recommendations, technical specifications, and annual reports of NIST’s cybersecurity activities.SP 800 publications are developed to address and support the security and privacy needs of U.S. Federal Government information and information systems. NIST develops SP 800-series publications in accordance with its statutory responsibilities under the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA) of 2014, 44 U.S.C. § 3551 et seq., Public Law (P.L.) 113-283.” - NIST Compliance FAQs: Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS)
“FIPS are standards and guidelines for federal computer systems that are developed by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in accordance with the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) and approved by the Secretary of Commerce. These standards and guidelines are developed when there are no acceptable industry standards or solutions for a particular government requirement. Although FIPS are developed for use by the federal government, many in the private sector voluntarily use these standards.” - National Vulnerability Database (NVD) Metadata Submission Guidelines for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) Numbering Authorities (CNAs) and Authorized Data Publishers
“The purpose of this document is to leverage the strength of technical knowledge provided by the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) Numbering Authorities (CNAs) and the application of consistent and unbiased CVE metadata provided by the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) analysts through the formalization of a CVE metadata submission process.” - VISA: PCI DSS Compliance
“Learn about Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) with Visa. Keep your cardholders safe with the latest security standards.” - OASIS
“One of the most respected, non-profit standards bodies in the world, OASIS Open offers projects—including open source projects—a path to standardization and de jure approval for reference in international policy and procurement.OASIS has a broad technical agenda encompassing cybersecurity, blockchain, privacy, cryptography, cloud computing, IoT, urban mobility, emergency management, content technologies. In fact, any initiative for developing code, APIs, specifications, or reference implementations can find a home at OASIS.” - OWASP Foundation
“The Open Web Application Security Project® (OWASP) is a nonprofit foundation that works to improve the security of software. Through community-led open source software projects, hundreds of local chapters worldwide, tens of thousands of members, and leading educational and training conferences, the OWASP Foundation is the source for developers and technologists to secure the web.” - Smart TV/device risks:
- digitaltrends: Freaked out by the FBI’s smart TV warning? Here’s what you should do
- Business Insider: The FBI just issued a warning about the risks of owning a smart TV — here are its suggestions for protecting your privacy
- USA Today: Is your smart TV too wise? The FBI warns your screen is watching you
- TechCrunch: Now even the FBI is warning about your smart TV’s security
- FBI Portland: Oregon FBI Tech Tuesday: Securing Smart TVs
- ZDNet: FBI recommends that you keep your IoT devices on a separate network
- Amazon Fixes Alexa Glitch That Could Have Divulged Personal Data
- That news story about the Iowa pentesters paid to break into a courthouse:
- Privacy:
- Computerworld: Snooping into a co-worker’s e-mail? You could be arrested
- 5 biggest GDPR fines so far [2020]
- Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- Privacy, Free Speech, and the Patriot Act: First and Fourth Amendment Limits on National Security Letters
- HITECH Act Enforcement Interim Final Rule
- HIPAA Turns 10: Analyzing the Past, Present and Future Impact
- TechCrunch: Google-Fitbit deal to be scrutinized in Europe over data competition concerns
- Consumer Watchdog Sues Zoom on Behalf of Public for Allegedly Deceiving Users about Privacy Protections
- Chiiiiiiiiiina:
- Intellectual property cases:
- Kylie Jenner Trademarks ‘Kylie Con’ And ‘Kylie Museum,’ Hinting Next Steps For Her Empire
- Apple Corps v Apple Computer
- Blue Ivy Carter: Not The First Of Jay-Z’s Trademark Blues
- Can You Trademark a Color?
- T-Mobile Has A Trademark On Magenta, Demands An Insurance Company Stop Using It
- T-Mobile says it owns exclusive rights to the color magenta
- Wal-Mart seeks smiley face rights
- Patent on a method for exercising a cat
- Patents and Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB) FAQs: Extension of Deadlines under the CARES Act
- Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF)
- How Unix Works: Become a Better Software Engineer
“Unix is beautiful. Allow me to paint some happy little trees for you. I’m not going to explain a bunch of commands – that’s boring, and there’s a million tutorials on the web doing that already. I’m going to leave you with the ability to reason about the system.Every fancy thing you want done is one google search away.
But understanding why the solution does what you want is not the same.That’s what gives you real power, the power to not be afraid. And since it rhymes, it must be true.” 
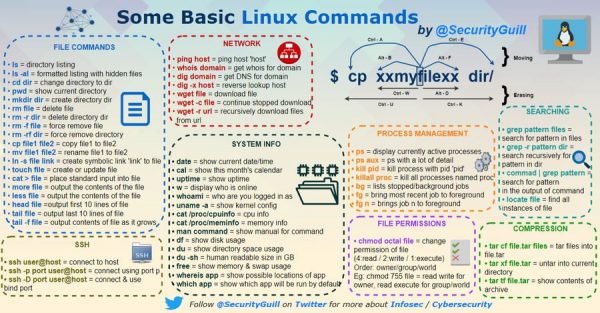
- Unixy goodness
- Julia “b0rk” Evans’ guides:
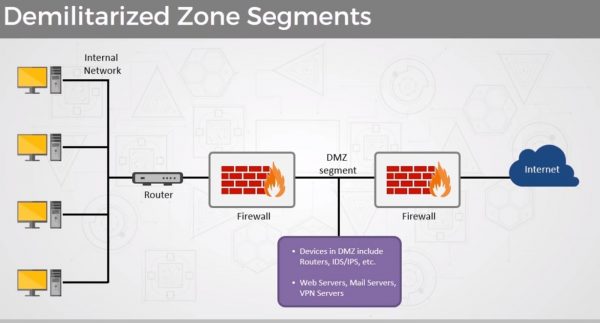
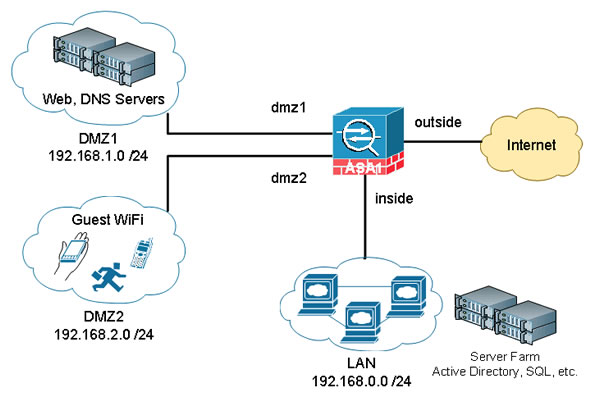
- DMZs
- Kaspersky: What is a honeypot?
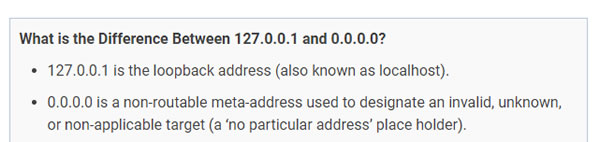
“In computer security terms, a cyber honeypot works in a similar way, baiting a trap for hackers. It’s a sacrificial computer system that’s intended to attract cyberattacks, like a decoy. It mimics a target for hackers, and uses their intrusion attempts to gain information about cybercriminals and the way they are operating or to distract them from other targets.” - IP addresses

- CyberChef
The Cyber Swiss Army Knife – a web app for encryption, encoding, compression and data analysis. - Which hash/encryption type is used by Kali Linux for /etc/shadow by default?
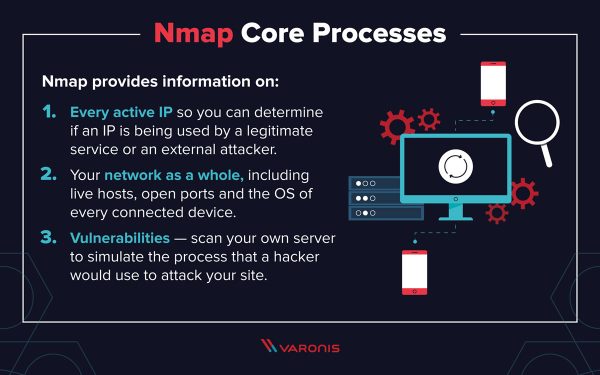
- nmap
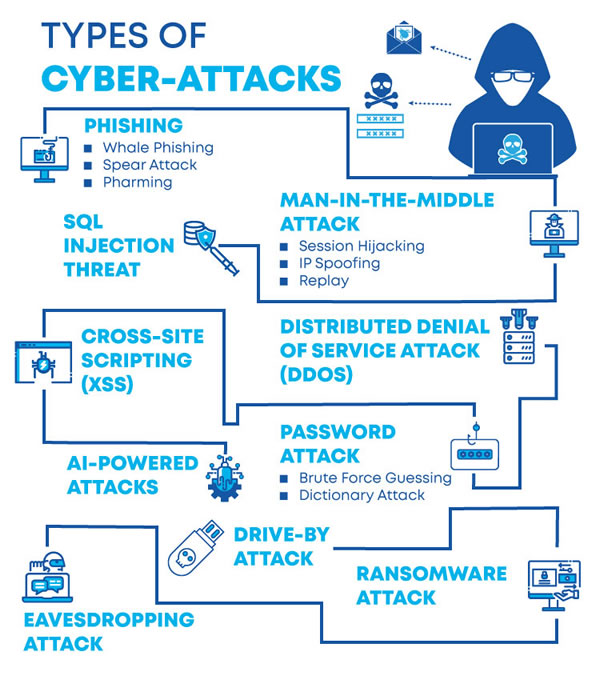
- Malware and attacks
- robots.txt:
- Photos and forensics:
- Tools:
- Wired: The Quest to Liberate $300,000 of Bitcoin From an Old Zip File
- Naughty Korea:
- SANS reading
- DISC personality profiles:
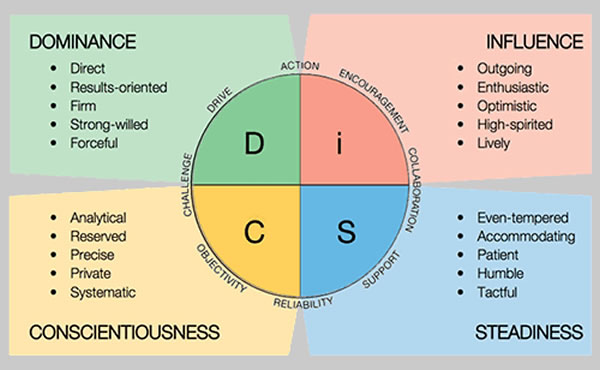
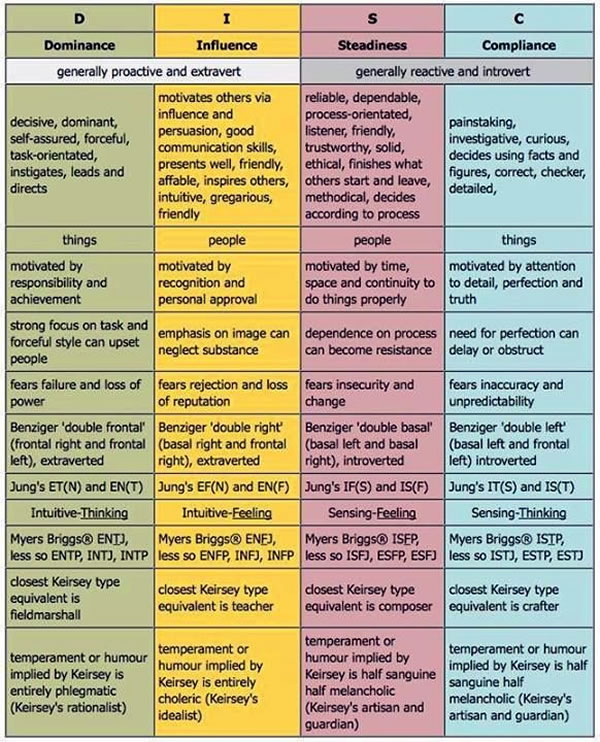
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: Cyber Security Guidance Material
A collection of “educational materials specifically designed to give HIPAA covered entities and business associates insight into how to respond to a cyber-related security incidents.” - DFIR — Digital Forensics and Incident Response
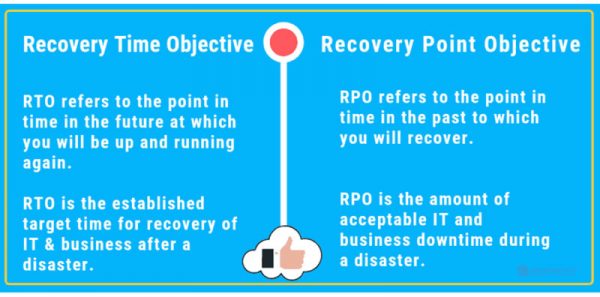
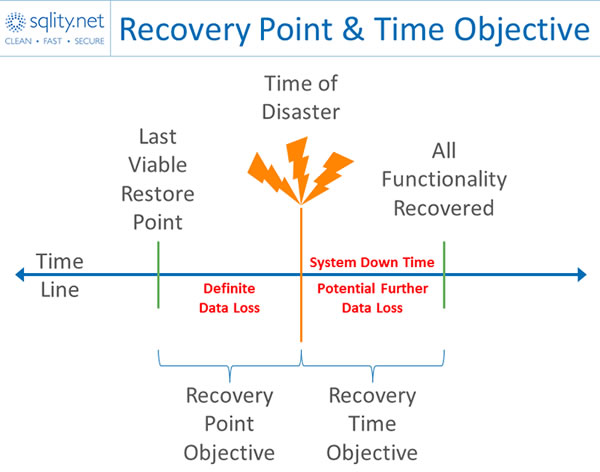
“Digital forensics and incident response is an important part of business and law enforcement operations. It is a philosophy supported by today’s advanced technology to offer a comprehensive solution for IT security professionals who seek to provide fully secure coverage of a corporation’s internal systems.” - Understanding RPO and RTO
“Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are two of the most important parameters of a disaster recovery or data protection plan. These are objectives which can guide enterprises to choose an optimal data backup plan.”
- The 3-2-1 backup rule
“For a one-computer user, the VMware backup strategy can be as simple as copying all important files to another device – or, ideally, several devices – and keeping them in a safe place. However, for multiple computer systems, things can be (and usually are) much more complicated, especially when it comes to virtual environments containing thousands of virtual machines. To protect physical machines, you would need to perform Windows Server backup or Linux Server backup, which might be difficult without effective backup tools. In these cases, a comprehensive data protection plan should include the 3-2-1 backup rule.”
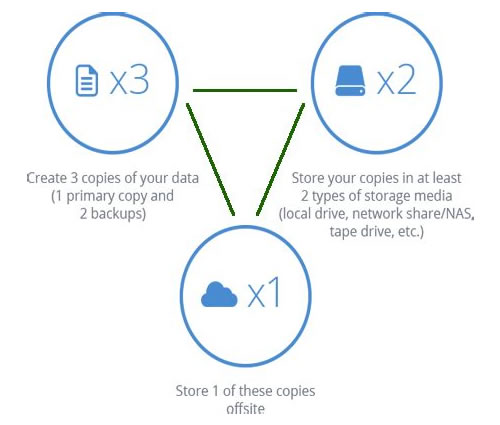
- What is BCDR? Business continuity and disaster recovery guide
“In this climate, business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) has a higher profile than ever before. Every organization, from small operations to the largest enterprises, is increasingly dependent on digital technologies to generate revenue, provide services and support customers who always expect applications and data to be available.” - How to Set Up an AI R&D Lab
“The moment a hyped-up new technology garners mainstream attention, many businesses will scramble to incorporate it into their enterprise. The majority of these trends will splutter and die out by Q4. Artificial intelligence (AI) is unlikely to be one of them.AI is a transformative series of tools that can accelerate productivity, drive insight, and open up unexplored revenue streams. It’s poised to revolutionize the way we do business and everyone in a leadership role should be thinking about it.But few organizations are set up to do AI properly.” - Tampa Bay:
- SANS Institute, which drills cyber professionals in defense, suffers breach
“The SANS Institute, which trains cybersecurity professionals around the world, was hacked, resulting in the compromise of 28,000 records.” - MITRE:
- ZDNet: FBI and NSA expose new Linux malware Drovorub, used by Russian state hackers
“The FBI and NSA have published today a joint security alert containing details about a new strain of Linux malware that the two agencies say was developed and deployed in real-world attacks by Russia’s military hackers.The two agencies say Russian hackers used the malware, named Drovorub, was to plant backdoors inside hacked networks.” - Military Cyber Professionals Association (MCPA)
“Military Cyber Professionals Association (MCPA) are a team of Soldiers, Sailors, Airmen, Marines, Veterans and others interested in the development of the American military cyber profession.Our members are interdisciplinary, as such a diverse set of perspectives is needed to develop cyberspace as an entire domain. Also included in our ranks are other government employees, contractors, academics, industry leaders, foreign allies, and private citizens.” - Protect your business from floods
Follow these recommendations to reduce the likelihood of flood damage to your business. - Mean Time to Recovery (MTR)
Mean time to recovery (MTTR) is the average time that a device will take to recover from any failure. - Why the fuck was I breached?
“Did you just lose 100m customer SSNs because your root password was ‘password’, you set an S3 bucket to public or you didn’t patch a well known vulnerability for 8 months? Is the media and government chewing you out because of it? Worry not! Our free excuse generator will help you develop an air-tight breach statement in no time!” - Penetration Test vs. Red Team Assessment: The Age Old Debate of Pirates vs. Ninjas Continues
“In a fight between pirates and ninjas, who would win? I know what you are thinking. “What in the world does this have to do with security?” Read on to find out but first, make a choice: Pirates or Ninjas?”

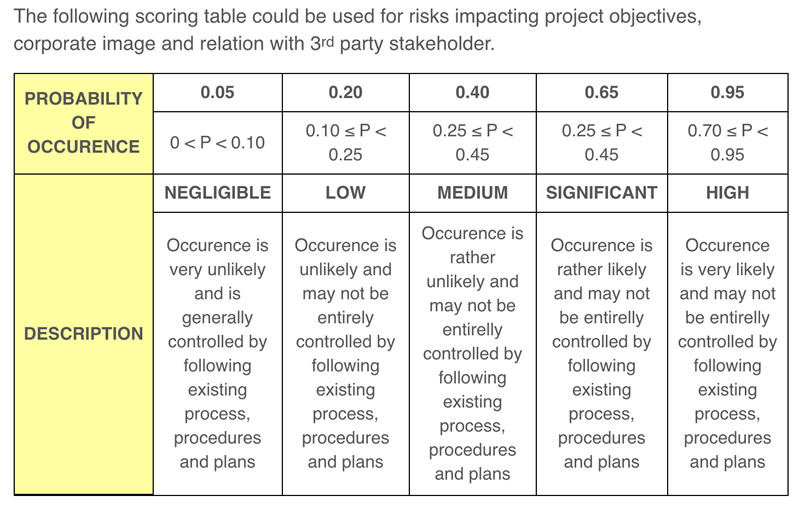
- Evaluating Risks Using Quantitative Risk Analysis
“Project managers should be prepared to perform different types of risk analysis. For many projects, the quicker qualitative risk assessment is all you need. But there are occasions when you will benefit from a quantitative risk analysis.Let’s take a look at this type of analysis: What is it? Why should we perform it? When should it be performed? And how do we quantify risks?”
- What is CMMI? A model for optimizing development processes
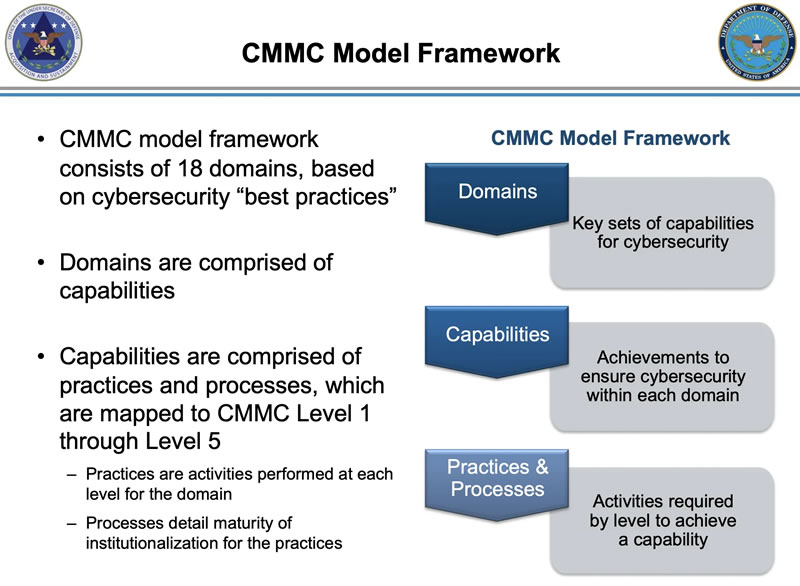
“The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a process and behavioral model that helps organizations streamline process improvement and encourage productive, efficient behaviors that decrease risks in software, product and service development.” - CMMC
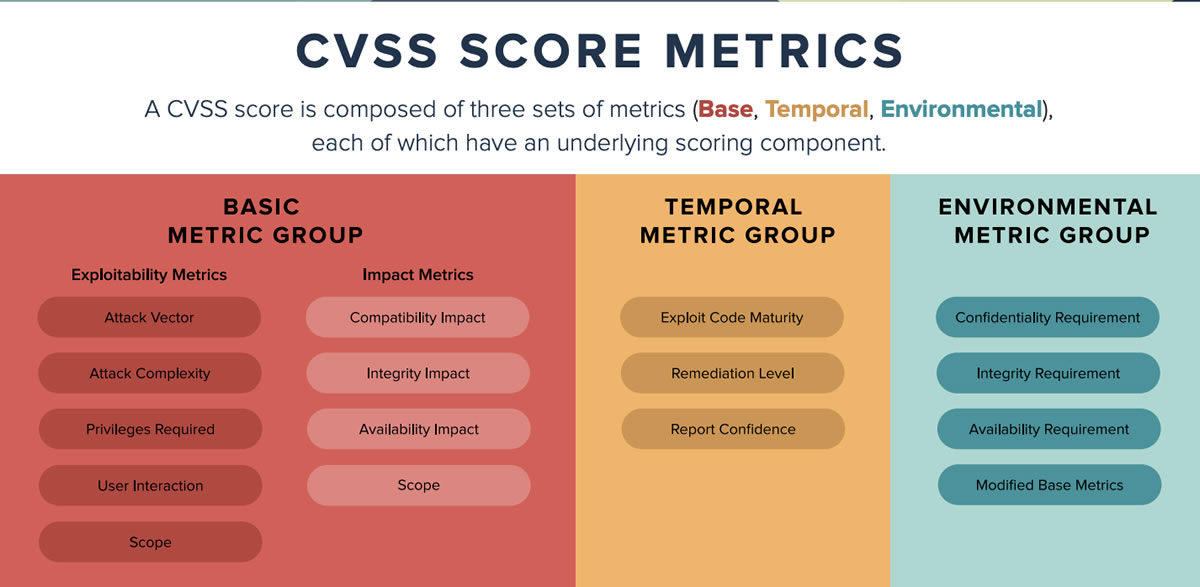
- CVSS
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard for assessing the severity of computer system security vulnerabilities.
- Is CVSS the Right Standard for Prioritization?
- CVSS calculator
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System
- Risk assessment and management:
- ISO 31000 — Risk Management
- ISO 31000:2009 — Risk management — Principles and guidelines
- Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations: A System Life Cycle Approach for Security and Privacy
- Mitigating Cybersecurity Risks & Compliance with NIST SP 800-37 Revision 2
- Summary Thoughts On NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-37 Revision 2 (Draft)
- OCTAVE risk assessment method examined up close
- Residual risk
- CISO
- How Many Email Accounts Do You Need?
“With all this need for email accounts, the question obviously arises: how many email accounts should you have? In theory, you could use a single email address for everything, but that could leave you with thousands upon thousands of emails from hundreds of sources in a single account; even with an account that allows you to easily sort everything, you’ll quickly be overwhelmed. It’s all but required that you have multiple email addresses nowadays.” - NIST NVD (National Vulnerability Database) — Vulnerability Metrics
“The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is an open framework for communicating the characteristics and severity of software vulnerabilities. CVSS consists of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental. The Base metrics produce a score ranging from 0 to 10, which can then be modified by scoring the Temporal and Environmental metrics. A CVSS score is also represented as a vector string, a compressed textual representation of the values used to derive the score. Thus, CVSS is well suited as a standard measurement system for industries, organizations, and governments that need accurate and consistent vulnerability severity scores. Two common uses of CVSS are calculating the severity of vulnerabilities discovered on one’s systems and as a factor in prioritization of vulnerability remediation activities. The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) provides CVSS scores for almost all known vulnerabilities.” - Tampa Bay UX Group
The Tampa Bay User Experience Group is one of the largest volunteer led user experience professional organizations in south central Florida. Krissy Scoufis created the group in August, 2013 with the goal of providing a network of design practitioners, product owners, web developers and product strategists who could share UX methodologies, principles and techniques. Mike Gallers and Beth Galambos joined the leadership team shortly after the group started and together they have hosted over 73 events. The group’s foundational pillars are to provide free mentorship, education and community to evangelize the User Experience discipline. Frequently partnering with other regional technology meetups, the Tampa Bay UX Meetup group has fostered a cross functional network of professionals dedicated to putting users at the center of product strategy and design. - People and communication skills
- 6 reasons why participation is important [community engagement]
- What Is Tone of Voice and Why Does It Matter?
- Body Language: Picking Up and Understanding Nonverbal Signals
- Interview Preparation Tips: Body Language During Interview
- 5 Ways To Avoid A Massive Email Misunderstanding
- 10 Simple Ways to Make People Like You More
- Radical Candor
- The Five Steps of Incident Response
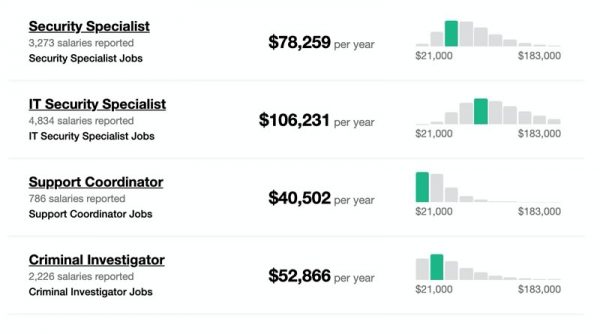
“Incident response is a process, not an isolated event. In order for incident response to be successful, teams should take a coordinated and organized approach to any incident. There are five important steps that every response program should cover in order to effectively address the wide range of security incidents that a company could experience.” - Cybersecurity jobs
- So-called “zero logs” VPNs
- Vulnerabilities and attacks
- What does “insecure by design” actually mean for OT/ICS security?
- Most Common Cyber Vulnerabilities Part 5 (Security Misconfiguration)
- The Big Hack: How China Used a Tiny Chip to Infiltrate U.S. Companies
- Shark Tank’s Barbara Corcoran Loses Nearly $400,000 in Cybersecurity Attack
- WASC threat classification taxonomy
- Most Common Web Application Attacks and How to Defend Against Them
- Hacker Lexicon: What Is a Side Channel Attack?
- What is a side channel attack? How these end-runs around encryption put everyone at risk
- What is a fileless attack? How hackers invade systems without installing software
- Unrestricted File Upload
- File-based attack
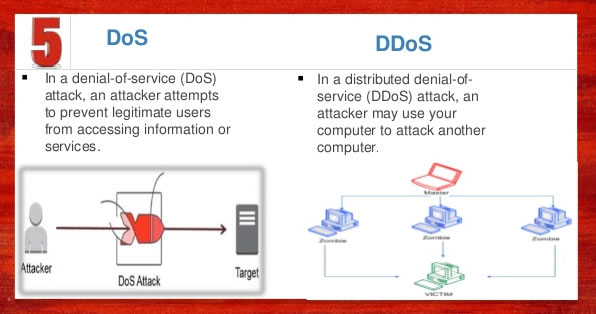
- Dos vs DDoS Attacks: The Differences and How To Prevent Them
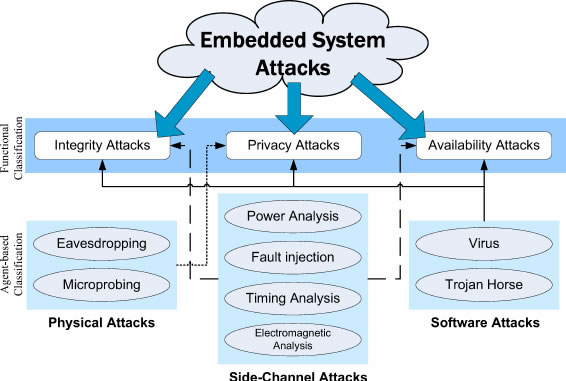
- Security in the Embedded System: Attacks and Countermeasures
- Provenance and pedigree
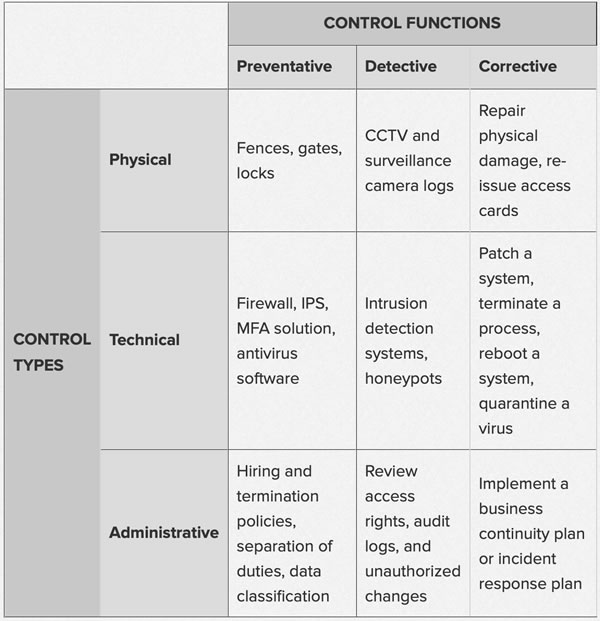
- What Are Security Controls?
“At the most fundamental level, IT security is about protecting things that are of value to an organization. That generally includes people, property, and data—in other words, the organization’s assets.Security controls exist to reduce or mitigate the risk to those assets. They include any type of policy, procedure, technique, method, solution, plan, action, or device designed to help accomplish that goal. Recognizable examples include firewalls, surveillance systems, and antivirus software.”
- 110 Must-Know Cybersecurity Statistics for 2020
“In order to give you a better idea of the current state of overall security, we’ve compiled the 110 must-know cybersecurity statistics for 2020. Hopefully, this will help you paint a picture of how potentially dire leaving your company insecure can be as well as show the prevalence and need for cybersecurity in business. This includes data breaches, hacking stats, different types of cybercrime, industry-specific stats, spending, costs and the cybersecurity career field.” - How to Restore Deleted Files Even After Emptying the Recycle Bin
“So you’ve emptied your recycle bin and then realized that you’ve deleted a file that you still need. If you act fast enough, you may be able to recover the files before the computer overwrites them with something else.Read on below for how to restore deleted files and for recycle bin recovery steps even when emptied.” - Splunk Training + Certification
You know I’m doing this next. - Reading material
- False Claims Act
- Wikipedia on the False Claims Act
- Justice.com on the False Claims Act
- False Claims Act stats
- Qui Tam
- Bradken Inc. pays $10.8 million to settle False Claims Act allegations and enters into deferred prosecution agreement
- Justice Department Recovers Over $2.8 Billion from False Claims Act Cases in Fiscal Year 2018
- Bradken Inc. pays $10.8 million to settle False Claims Act allegations and enters into deferred prosecution agreement
- Justice Department Recovers Over $2.8 Billion from False Claims Act Cases in Fiscal Year 2018
- Beyond the False Claims Act: The Government’s Untraditional Tools in Health Care Fraud Prosecutions
- False Claims Act Settlements Top $200 Million in the Past Week
- Oklahoma City Hospital, Management Company, And Physician Group To Pay $72.3 Million To Settle Federal And State False Claims Act Allegations Arising From Improper Payments To Referring Physicians
- Universal Health Services, Inc. And Related Entities To Pay $122 Million To Settle False Claims Act Allegations Relating To Medically Unnecessary Inpatient Behavioral Health Services And Illegal Kickbacks
- Twenty-Seven Skilled Nursing Facilities Controlled By Longwood Management Corporation To Pay $16.7 Million To Resolve False Claims Act Allegations
- 2020 False Claims Act Penalties
- MiMedx Group Inc. Agrees to Pay $6.5 Million to Resolve False Claims Act Allegations of False Commercial Pricing Disclosures
- DOJ Agrees to Civil Settlement with Additional Firm Involved in Bid Rigging and Fraud Targeting Defense Department Fuel Supply Contracts for U.S. Military Bases in South Korea
- Contract Rehab Provider to Pay $4 Million to Resolve False Claims Act Allegations Relating to the Provision of Medically Unnecessary Rehabilitation Therapy Services
- APT — Advanced Persistent Threat
- Malware
- Vishing
- Magecart
- What is Magecart? How this hacker group steals payment card data
Hacking groups that make up Magecart are effective and persistent at stealing customer and payment card data through skimmers. Here’s how they work and what you can do to mitigate the risk. - Magecart Hacker Group Hits 17,000 Domains—and Counting
- What is Magecart? How this hacker group steals payment card data
- OWASP Top Ten
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document for developers and web application security. It represents a broad consensus about the most critical security risks to web applications.
- CVEs
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures
- An Ontology-based Approach to Model Common
Vulnerabilities and Exposures in Information Security - The CWE/SANS Top 25 Security Vulnerabilities: What They Mean for Embedded Developers
- CWE/SANS TOP 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors
- Open Source Vulnerability Databases
- Injection attacks
- SQL injection
- Basic SQL Injection Attack
- SQL Injection Prevention Cheat Sheet
- Blind SQL Injection
- OS command injection
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- Input Validation Errors: The Root of All Evil in Web Applications
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Explained and Preventing XSS Attacks
- Cross Site Scripting Prevention Cheat Sheet
- Cross site request forgery (CSRF) attack
- XSS vs CSRF
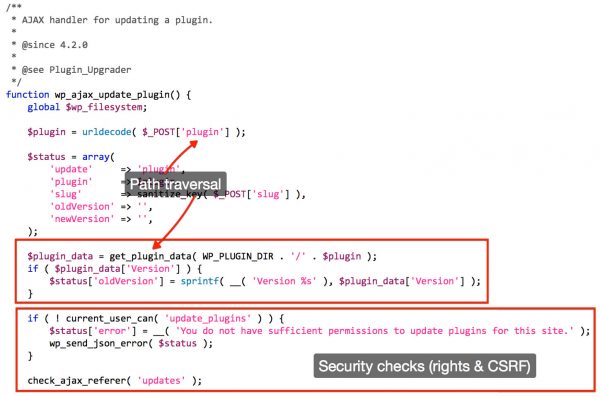
- Path Traversal
- Buffer/stack overflows
- Here are six basic human tendencies that are exploited in social engineering attacks:
- Authority: An attacker may call you pretending to be an executive in order to exploit your tendency to comply with authority figures.
- Liking: An attacker may try to build rapport with you by finding common interests, and then ask you for a “favor”.
- Reciprocation: An attacker may try to do something for you, or convince you that he or she has, before asking you for something in return.
- Consistency: An attacker might first get your verbal commitment to abide by a fake security policy, knowing that once you agree to do so, you will likely follow through with his next request in order to keep your word.
- Social Validation: An attacker may try to convince you to participate in a fake survey by telling you that others in your department already have. He or she may have even gotten some of their names and use them to gain your trust.
- Scarcity: An attacker may tell you that the first 10 people to complete a survey will automatically win a prize and that since some of your co-workers have already taken the survey, you might as well too.
- Social Studies – A Lesson in Social Engineering Basics
As we have become more and more vigilant against clicking on malicious links in suspicious emails, some social engineers have gone back to the classic person-to-person approach. Their basic strategy is to prey on vulnerabilities in human nature.