Here’s a blast from the past, courtesy of Scootinger’s Blog:
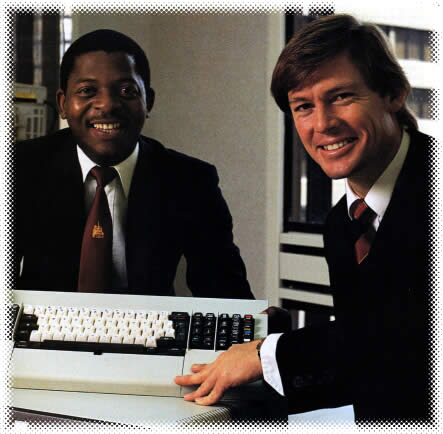
This is a Mac user vs. PC user comparison from the September 1996 issue of MacAddict. (this issue was actually the premiere/first issue of MacAddict) I recently found it when going through some of my old MacAddict magazines. It doesn’t look a lot different from the “I’m a PC and I’m a Mac” Apple ads of today, at least in my opinion!
The whole “PC users wear suits” thing is a long-standing artifact of the corporate culture of IBM, the originator of the PC. Our younger readers — and I sigh as I realize that by “younger”, I mean “those of you in your twenties or younger” — may be unaware of the legends of IBM attire. For decades, the company’s dress code — strictly enforced even though it was unwritten — was that of a right-wing lobbyist: dark suit, whie shirt, conservative tie and wing-tip shoes. Here’s an excerpt from a 1995 International Herald Tribune story that covered IBM’s relaxing of its dress code:
Jonathan B. Dick, a company lawyer, came to work at IBM’s headquarters in Armonk, New York, this week wearing a white fisherman’s sweater, black jeans and wrinkled tan boots, The New York Times reports. He recalls that on his first day at work 17 years ago he wore a dark suit, white shirt and conservative tie – all part of the standard IBM uniform – and loafers. His boss asked, “Why did you wear your bedroom slippers to work?” He was given the rest of the day off to shop for a pair of wing tips.
For the really curious, IBM actually has a section of its site devoted to pictures of IBM attire over the years. Here’s one from 1984:
Women IBMers adapted the standard dress code and made it their own. Here’s a marketing rep from 1979:
Apple, on the other hand, being a company founded in the 1970s in the Bay Area, took a more relaxed attitude to office attire and were one of the first companies to be known for allowing casual clothes in the workplace. Their only “suit” of note was Gil Amelio, and as Guy Kawasaki remarked at a keynote at a Macromedia User Conference in the late 1990s, even he understood the need to keep letting Apple employees wear jeans:

One last tidbit of info: if you’d like to dress just like the “Mac” guy from the “I’m a PC, I’m a Mac” ads, the LifeClever blog has an article telling you where to shop to get the “I’m a Mac” look:
I’m a little late in highlighting something Steve “Micro Persuasion” Rubel posted in his blog last week while he ruminated on Robert Cringley’s suggestion that Apple should embed BitTorrent support into the Apple TV box.
However, Cringley raises a heckuva an idea that somebody, most likely not Apple, will pursue. A tandem of services are coming together that will leverage the grid to open TV up as a content distribution channel for the masses. However, this won’t come from Apple at first. The innovation will start with enthusiasts, arising from the edge of the network not the center. Just as it did with PCs and the Internet.
Already all the technology is in place for you to cut your cable and go IP if you wanted to (although you will miss it because of content). Right now it is very kludgy and really only for geeks. Take a small box like a Mac Mini and attach it to your TV – like Dave did. Then throw in a very fast connection, an app like Democracy and a file sharing system that runs off BitTorrent and you have an IPTV that bypasses your cable company.
Democracy for discovery, BitTorrent for distribution, slap some Google advertising on the thing to add revenue, and hey-presto, you’re sticking it to The Media Man. It’s the Broadband Bypass.
Unfortunately, like communism, and using Linux on the desktop, file this idea under “good in theory.” It suffers from focusing on the means of production rather than the real purpose of the whole thing, and it’s a little weird that people still find the idea of p2p for content delivery so enthralling.
Yes, it appears there are still some enthusiasts out there for the idea that “The Grid of Tomorrow” will inevitably replace the one-to-many content distribution architecture of the internet today. While the idea of an IP video network that doesn’t have to worry about the cost of bandwidth both sounds good and is technically feasible I question whether it benefits customers enough to be a serious threat to established media companies.
If I’m Joost or BitTorrent.com, it’s clear that a grid-based content distribution network built on a peer-to-peer network is a great way to bootstrap since you don’t have to worry about provisioning bandwidth for projected peak traffic. In the event of sudden success, scaling out to meet demand doesn’t bother you at all, since the users are providing the infrastructure. Even so, this isn’t enough to guarantee success, it just lowers the costs of failure. This is why Joost and BitTorrent.com are doing everything they can to sign premium content deals for their respective services.
For their part, Viacom’s deal with Joost isn’t about end-running the cable companies or the broadcast networks. They could care less about the bandwidth value proposition offered by Joost’s p2p network. They just want to pursue every outlet possible on their terms (ie, with DRM and a big slice of the revenue model).
As Viacom supremo Philippe Dauman said in a Wall Street Journal article on the deal:
“We’re interested in distribution of our content on as many platforms as possible, provided we can operate in a secure environment,” Viacom Chief Executive Philippe Dauman said in an interview. “This assures any potential partners that we’re open for business and that we’re able to enter into transactions with companies that respect our content and the considerations of our business.”
For Viacom, it’s a chip in the game with Google. They’re signalling that they can do business with a number of partners (Joost, Apple), and they can go it alone, too.
Joost may be getting a lot of heat because they’re building atop a p2p architecture, but that’s merely cheap means to a business end for Joost. They want to be the way people using computers watch TV, and this is the least expensive way for them to get there. Apple has similar ambitions, but they’re a $20 billion/year company with a hardware business; moving to a p2p delivery network wouldn’t make a real difference to them. Both companies, and a few others, have a real chance at becoming the main aggregators of digital content, but the content delivery architecture underpinning their services isn’t the critical factor to their success. Ultimately, it will come down to the strength of the library on offer, and the simplicity of the customer experience.
Source: Micro Persuasion: Grid-Powered IPTV is Coming, But Not from Apple
[via Gizmodo] Here’s an interesting segment from the Today show in which Forbes managing editor Dennis Kneale participated in a feature called Could You Do Without? In it, he took the challenge of going without his mobile phone, Blackberry, email and internet access for a week. He missed appointments, bounced a couple of checks (since he was unable to do online banking), ran late for meetings (since his cellphone was also his watch) and after not being reachable by his six-year-old daughter who has committed his cellphone number to memory, broke down in tears. He’s pretty good-natured about it at the end, though — in the post-challenge interview with Matt Lauer, he says that the Forbes ad department is probably coming up with new slogans like “Read Forbes: We’re edited by crybabies!”
![]()
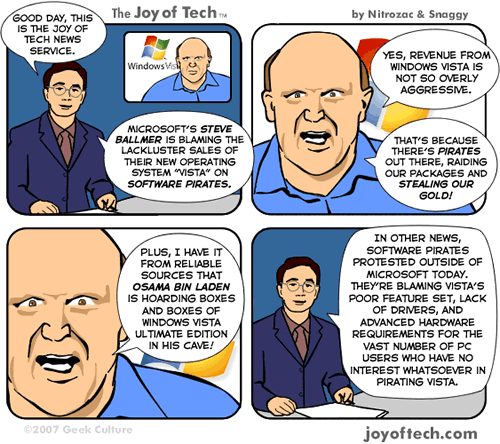
And here I thought that The Police’s upcoming concert tour was going to be this year’s most unlikely onstage gathering of guys who have trouble getting along, butI think that’s going to get outdone by Bill Gates’ and Steve Jobs’ joint appearance at the Wall Street Journal’s “D: All Things Digital” conference taking place at the end of May. According to the news release, “The two men will jointly discuss the history and future of the digital revolution in an unrehearsed, unscripted, onstage conversation.”
This should be amusing. Jobs has the benefits of Apple’s strong performance this decade among both ordinary users and alpha geeks, stage presence, improvisation skills and the Reality Distortion Field. On the other hand, Gates has the contend with the lackluster sales and reviews of both Windows Vista and the Zune. Making matters worse, if his recent appearance and awkwardly abrupt exit from The Daily Show are any indication, Gates is still uncomfortable conversing with carbon-based life forms and even more so when the conversation hasn’t been pre-programmed.
In ZDNet’s Gear for Geeks, Adrian Kingsley-Hughes writes about Dell’s newly-launched IdeaStorm site, a site where users can make suggestions about products and features they’d like to see from Dell. “Some of the ideas are pretty obvious,” he writes, “and Dell could have found out what people wanted by doing a quick web search, but some of the other ideas are interesting and show how the PC industry is changing and how Dell’s business model is lagging behind what their customers want.”
What do Dell customers want? According to Kingsley-Hughes, they want:
- Linux pre-installed. On the IdeaStorm site, this request has been promoted (think of promotion as being similar to “digging” on Digg or “upvoting” on Reddit) some 31,000 times.
- OpenOffice pre-installed, either alongside or instead of Microsoft Office or Works. (Works is still available?)
- An option to just get a machine, without any additional software.
- 1GB RAM as the minimum offered with any machine.
- End offshore tech support.
- Stop installing additional “craplets” on top of the OS.
Links
If you’re already using Vista, you’ve probably run into at least one of those annoying “Cancel or Allow?” dialog boxes lampooned in the Mac ad above. Now it turns out that you can’t always trust them. The Symantec Security Response weblog has an article in which they say that in some cases, Vista’s UAC approach “becomes a chicken and egg situation when the user is making a decision based on a false sense of trust.”
The article’s a little bit on the technical side; I’ll translate it into layperson’s terms and post something later today.